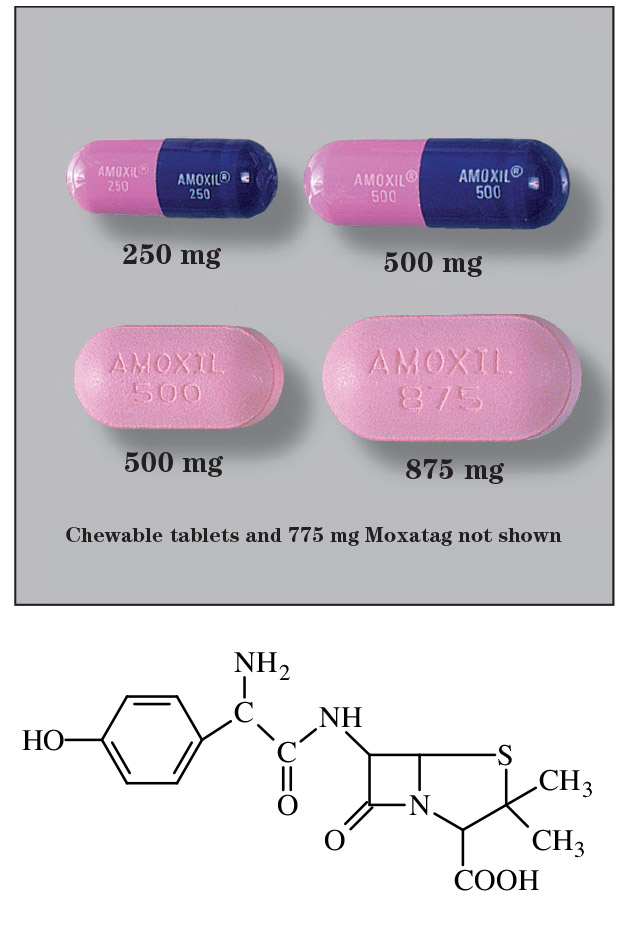
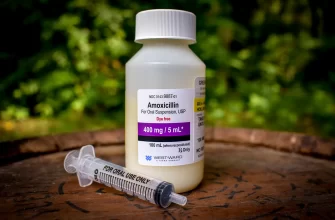
Need amoxicillin but unsure which form is right for you? Let’s clarify your options. Amoxicillin is available in several forms to suit different needs and preferences.
Oral forms dominate, including capsules, tablets, and chewable dispersible tablets for easier administration, particularly for children. The choice often depends on individual tolerance and dosage requirements. Always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions regarding dosage and frequency.
Liquid suspensions offer another common option, especially convenient for those who have difficulty swallowing pills or for young children. These are generally formulated with a pleasant taste, although individual sensitivities vary. Remember to shake the suspension well before each dose to ensure uniform medication distribution.
Less common, but available in specific circumstances, is intravenous amoxicillin. This method is usually reserved for serious infections or when oral administration isn’t feasible. A healthcare professional will administer this form directly into a vein.
- Other Forms of Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin Capsules: Dosage and Considerations
- Amoxicillin Tablets: Chewable, Dispersible, and Extended-Release Options
- Amoxicillin Liquid Suspension: Preparation and Storage Guidelines
- Amoxicillin Powder for Oral Suspension: Reconstitution and Shelf Life
- Reconstitution
- Shelf Life
- Proper Storage
- Amoxicillin Injection: Administration and Precautions
- Intramuscular Injection Technique
- Important Precautions
- Post-Injection Monitoring
- Amoxicillin in Combination Products: Common Combinations and Uses
- Common Amoxicillin Combinations
- Uses Based on Combination
- Important Considerations
Other Forms of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is available in several forms to suit different needs. You’ll find it as capsules, tablets, and chewable tablets for oral administration. Liquid suspensions offer flexibility, particularly for children and individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills. These suspensions often come with a measuring device for accurate dosing.
Powder for oral suspension requires mixing with water before use; follow the package instructions carefully for accurate concentration. This form allows for a customized dosage, especially convenient for children requiring varying amounts of medication.
Intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM) injections provide a direct route for faster absorption when oral administration isn’t feasible. This is often used in hospitals for severe infections requiring immediate treatment.
The choice of amoxicillin form depends on individual factors like age, swallowing ability, and severity of infection. Consult your doctor or pharmacist to determine the best formulation for your specific situation. They can guide you on the appropriate dosage and administration method.
Amoxicillin Capsules: Dosage and Considerations
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. A typical adult dose is 250-500mg every 8 hours, but this varies significantly based on the infection’s severity and your individual health. Children’s dosages are weight-based; consult your pediatrician for accurate guidance.
Take amoxicillin capsules with a full glass of water. Avoid taking them with dairy products or antacids, as these can hinder absorption. Food generally doesn’t affect absorption, but consistency is key for optimal results. Finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better, to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Severe allergic reactions are rare but serious; seek immediate medical attention if you experience hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications; inform your doctor of all other medicines, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you’re currently taking.
Store amoxicillin capsules at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Discard any unused medication after its expiration date. Regular blood tests might be necessary during prolonged treatment to monitor for any unexpected side effects. Proactive communication with your healthcare provider ensures safe and effective treatment.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance on amoxicillin capsule usage.
Disclaimer: This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Amoxicillin Tablets: Chewable, Dispersible, and Extended-Release Options
For children who struggle to swallow pills, chewable amoxicillin tablets offer a convenient solution. These tablets dissolve easily in the mouth, making medication time simpler. Always follow the prescribed dosage carefully.
Dispersible tablets provide another option for individuals with swallowing difficulties. Simply dissolve the tablet in water before administering. This ensures complete absorption of the medication.
Extended-release amoxicillin tablets provide a slower, more sustained release of the antibiotic into the bloodstream. This means fewer doses per day, improving convenience for patients. Consult your doctor regarding the appropriate extended-release option.
Amoxicillin Liquid Suspension: Preparation and Storage Guidelines
Always shake the bottle vigorously for at least 10-15 seconds before each use to ensure even distribution of the medication. This prevents uneven dosing.
Follow the prescription instructions carefully regarding dosage and frequency. Never exceed the recommended dose.
After reconstitution (mixing the powder with water), refrigerate the suspension. Discard any unused portion after 14 days. Do not freeze.
Use a measuring device provided with the medication, or use a calibrated oral syringe for precise dosing. Household spoons are inaccurate and should be avoided.
| Temperature | Storage Time |
|---|---|
| Refrigerated (36-46°F or 2-8°C) | Up to 14 days after reconstitution |
| Room temperature (68-77°F or 20-25°C) | Discard immediately; Do not use. |
Observe the suspension for any unusual changes in color, texture, or odor. Discard it if any of these occur. Report any concerns to your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep the medication out of reach of children. Proper storage is vital to maintain the medication’s potency and safety.
Amoxicillin Powder for Oral Suspension: Reconstitution and Shelf Life
Always follow the instructions on your amoxicillin powder for oral suspension label. Generally, you’ll add the specified amount of water to the powder bottle. Mix thoroughly to ensure complete dissolution.
Reconstitution
- Use only the type and amount of water indicated on the label. Using too much or too little water can affect the accuracy of the dosage.
- Shake the bottle vigorously for at least 15 seconds after adding water to ensure even distribution.
- After reconstitution, carefully check the appearance of the mixture for any unusual clumps or color changes. If you notice anything unexpected, discard the mixture and contact your pharmacist.
- Once mixed, refrigerate the suspension.
Shelf Life
The shelf life of reconstituted amoxicillin suspension varies. Check your label; it typically lasts for 7-14 days after reconstitution. Discard any remaining suspension after this timeframe, even if it appears unused. Discarding the suspension ensures you receive the correct dose. Discarding unused medication safely is important.
Proper Storage
- Refrigerate the reconstituted suspension at 36-46°F (2-8°C).
- Keep the suspension away from direct sunlight.
- Do not freeze the suspension.
- Always keep the medication out of reach of children.
Following these guidelines ensures your child receives the correct medication. If you have any questions about reconstitution or shelf life, consult your pharmacist or doctor.
Amoxicillin Injection: Administration and Precautions
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Amoxicillin injection is administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM), depending on the prescription. IV administration typically requires a healthcare professional, while IM injections can sometimes be self-administered under medical supervision. Dosage varies significantly based on the patient’s age, weight, and the infection’s severity. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
Intramuscular Injection Technique
For IM injections, use the correct needle size and injection site (usually the upper outer quadrant of the buttock or the thigh). Ensure the injection area is clean. Aspirate before injecting to avoid accidental injection into a blood vessel. Inject the medication slowly and steadily. Afterwards, gently massage the injection site. Report any unusual pain, swelling, or redness.
Important Precautions
Before receiving amoxicillin, inform your doctor about any allergies, particularly to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics. Report any existing kidney or liver problems. During treatment, monitor for allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing). Seek immediate medical attention if these occur. Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications; discuss all your medications with your doctor. Pregnancy and breastfeeding require special considerations; consult your physician before use.
Post-Injection Monitoring
After the injection, observe for any adverse effects for at least 30 minutes. Drink plenty of fluids to aid in excretion of the medication. Proper disposal of used needles is crucial; follow guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
Amoxicillin in Combination Products: Common Combinations and Uses
Amoxicillin frequently appears in combination with other drugs to enhance its efficacy and broaden its therapeutic range. Understanding these combinations is key to proper treatment.
Common Amoxicillin Combinations
- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (Augmentin): This is perhaps the most common combination. Clavulanate potassium inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes, which some bacteria produce to break down amoxicillin. This makes the combination effective against a wider range of bacteria, including those resistant to amoxicillin alone. It’s often prescribed for respiratory tract infections, ear infections, and skin infections.
- Amoxicillin/Probiotic Combinations: Some formulations include amoxicillin alongside probiotics, aiming to mitigate the potential disruption of gut flora often associated with antibiotic use. While research on their effectiveness varies, the intention is to support digestive health during treatment.
- Amoxicillin with other antibiotics (less common): While less frequent, amoxicillin can sometimes be combined with other antibiotics for specific infections where synergistic effects are desired. Always consult a physician for guidance on these less-common combinations.
Uses Based on Combination
- Respiratory Infections: Amoxicillin/clavulanate is a go-to treatment for various respiratory infections, particularly those caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.
- Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Amoxicillin, often in combination with clavulanate, is frequently used to treat ear infections in children and adults.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Amoxicillin/clavulanate proves effective against many bacteria causing skin infections. The choice of combination depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Dental Infections: Amoxicillin, sometimes in combination with other antibiotics, can be part of a treatment regimen for dental infections.
Remember: Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate amoxicillin combination and dosage for your specific condition. Self-medicating can be harmful. This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Important Considerations
- Allergies: Individuals with penicillin allergies should exercise extreme caution and inform their doctor before taking any amoxicillin-containing product.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Serious side effects are less common but require immediate medical attention.
- Dosage: Dosage varies depending on the individual’s age, weight, and the specific infection being treated. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.