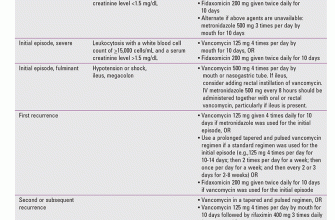
Metronidazole, commonly known as Flagyl, is a frequently prescribed antibiotic for treating diverticulitis, specifically for uncomplicated cases. This means it’s often effective for managing infections confined to the diverticula themselves, avoiding the need for surgery. Remember, always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Flagyl combats bacteria implicated in diverticulitis, reducing inflammation and resolving the infection. Typical treatment involves a course of oral medication. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration, which typically ranges from 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of your condition and your individual response to the treatment.
Important Note: While Flagyl is commonly used, it’s not suitable for all diverticulitis cases. Severe or complicated diverticulitis, including abscesses or fistulas, may require alternative treatment strategies, including intravenous antibiotics and possibly surgery. Side effects are possible and vary depending on the patient; they include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Discuss these possibilities with your doctor. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding medication usage and follow-up appointments.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
- Flagyl for Diverticulitis: A Comprehensive Guide
- Dosage and Administration
- Flagyl and Other Treatments
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Alternative Treatments
- What is Diverticulitis and How Does Flagyl Work?
- Flagyl Dosage and Administration for Diverticulitis
- Important Considerations:
- Dosage Forms:
- Potential Side Effects of Flagyl for Diverticulitis
- When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Complications and Alternative Treatments
- Flagyl and Other Medications: Potential Interactions
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Diverticulitis Treatment
Flagyl for Diverticulitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Metronidazole, commonly known as Flagyl, is a frequently prescribed antibiotic for diverticulitis treatment. It effectively targets bacteria often implicated in diverticular infections.
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor determines the appropriate Flagyl dosage based on your specific condition and health. Typical regimens involve oral administration for 7-10 days. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never alter dosage without consulting them. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Report any significant side effects immediately.
Flagyl and Other Treatments
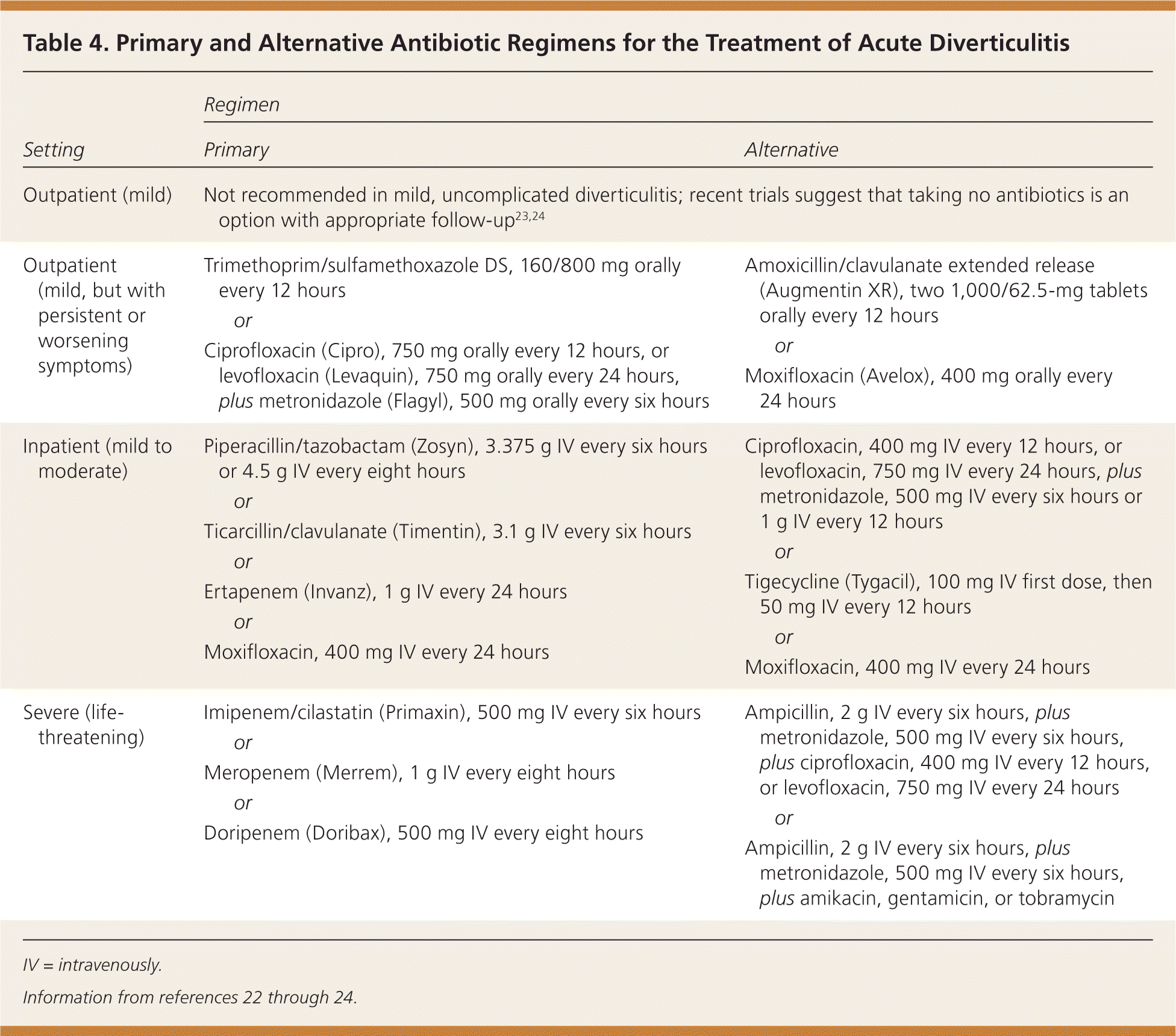
Flagyl is often used in conjunction with other treatments for diverticulitis, such as bowel rest (clear liquids only) and pain management. Severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics. Your physician will create a tailored treatment plan based on your needs.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience high fever, severe abdominal pain, or signs of peritonitis (abdominal rigidity, tenderness). These symptoms suggest a serious complication requiring prompt intervention.
Alternative Treatments
Note: This section is for informational purposes only and does not substitute medical advice. Alternatives to antibiotics may be considered for uncomplicated diverticulitis, such as dietary modifications or specific probiotics. Always discuss these options with your doctor before making changes to your treatment plan.
What is Diverticulitis and How Does Flagyl Work?
Diverticulitis is an inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) that can develop in your large intestine. These pouches usually form in weaker areas of the bowel wall. When they become inflamed or infected, it causes symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and changes in bowel habits. Severe cases can lead to complications requiring hospitalization.
Flagyl (metronidazole) is an antibiotic effective against several bacteria, including those often responsible for diverticulitis. It works by damaging the DNA of these bacteria, preventing their growth and reproduction. This helps clear the infection and reduce inflammation in your diverticula.
- Mechanism: Flagyl disrupts bacterial DNA replication and repair processes.
- Target Bacteria: It effectively targets Bacteroides fragilis and other anaerobic bacteria frequently implicated in diverticulitis.
- Administration: Flagyl is commonly prescribed as an oral medication, though intravenous administration may be necessary in severe cases.
Remember, Flagyl is a prescription drug. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration based on the severity of your diverticulitis. Always follow their instructions precisely and report any adverse reactions immediately.
- Consult your doctor: Self-treating diverticulitis is risky. A doctor can diagnose the condition accurately and tailor treatment to your needs.
- Complete the prescribed course: Stopping Flagyl prematurely might lead to recurrence of the infection.
- Monitor your symptoms: Contact your doctor if symptoms worsen or don’t improve after starting treatment.
While Flagyl is often successful in treating diverticulitis, it’s crucial to understand it’s not a cure for diverticulosis (the presence of diverticula). Lifestyle changes, like increasing fiber intake, may help prevent future episodes. Always seek professional medical advice regarding your health and treatment options.
Flagyl Dosage and Administration for Diverticulitis
Your doctor will determine the correct Flagyl (metronidazole) dosage based on your individual needs and the severity of your diverticulitis. Typical dosages range from 500 mg to 750 mg, administered orally every eight hours or twice daily. Treatment usually lasts seven to ten days.
Important Considerations:
Always follow your physician’s prescribed dosage and duration. Never alter your medication regimen without consulting your doctor. Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you feel better sooner. This prevents potential recurrence of the infection. Report any side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, to your doctor immediately. Flagyl can interact with certain medications, so inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Alcohol consumption should be avoided during treatment and for several days afterward, as it can cause unpleasant side effects. If you experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, or other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Dosage Forms:
Flagyl is available in various forms, including tablets and capsules. Your doctor will prescribe the most suitable form for you. Always take the medication as directed on the prescription label or by your physician.
Potential Side Effects of Flagyl for Diverticulitis
Flagyl, or metronidazole, effectively treats diverticulitis infections, but it can cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These usually are mild and resolve without intervention.
Some individuals experience a metallic taste in their mouth. This is a fairly common, though unpleasant, side effect. Drinking plenty of water may help.
More serious, though less frequent, side effects include seizures. If you experience convulsions or unusual neurological symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
A less common but significant side effect involves blood disorders. Report any unusual bruising, bleeding, or fatigue to your doctor immediately.
Peripheral neuropathy, characterized by tingling or numbness in the extremities, is another possible side effect. This is usually reversible upon cessation of the medication, but prompt reporting to your physician is crucial.
Allergic reactions, ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis, can occur. Symptoms like hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing require immediate emergency medical care.
During treatment with Flagyl, avoid alcohol consumption. This combination can cause a severe reaction.
Your doctor can discuss potential risks and benefits with you and help determine if Flagyl is the right treatment for your diverticulitis.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Complications and Alternative Treatments
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), severe abdominal pain worsening despite Flagyl use, or bloody stools. These could signal a serious complication like an abscess or perforation requiring immediate intervention.
Persistent symptoms after a week of Flagyl treatment warrant a doctor’s visit. Your physician may adjust the medication, order additional tests, or explore other treatment options. Don’t delay seeking help if your symptoms aren’t improving.
Alternative treatments for diverticulitis, sometimes used in conjunction with or after antibiotics, include high-fiber diets to promote regular bowel movements and reduce pressure on the diverticula. Your doctor can guide you on the appropriate dietary changes.
In some cases, minimally invasive procedures, such as colonoscopy, may be necessary to diagnose or treat complications like abscesses. Surgical intervention is sometimes required for severe cases, including perforation or fistula formation.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are vital, particularly after a bout of diverticulitis, to monitor your progress and prevent recurrence. Open communication with your healthcare provider ensures you receive the most appropriate care.
Flagyl and Other Medications: Potential Interactions
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before starting Flagyl. This includes prescription drugs for other conditions. Failure to do so could lead to harmful interactions.
Specific medications that may interact negatively with Flagyl include:
| Medication Type | Specific Examples | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants (blood thinners) | Warfarin (Coumadin) | Increased bleeding risk. Your doctor may need to monitor your blood clotting time more closely. |
| Lithium | Lithium carbonate | Increased lithium levels in your blood, potentially leading to toxicity. Regular blood tests are recommended. |
| Alcohol | Beer, wine, liquor | Severe nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Avoid alcohol completely while taking Flagyl. |
| Disulfiram (Antabuse) | Disulfiram | Similar effects to alcohol interaction; potentially dangerous. Consult your doctor before combining these medications. |
| Metronidazole (Flagyl) and other medications containing this active ingredient | Certain topical creams | Increased risk of side effects due to combined dosage. Your physician will determine appropriate adjustments, if necessary. |
This list isn’t exhaustive; other interactions are possible. Your physician can provide more tailored advice based on your specific health status and medication profile. Open communication with your doctor is key to preventing adverse reactions.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Diverticulitis Treatment
Increase your fiber intake gradually. Aim for 25-35 grams daily through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This helps regulate bowel movements and prevents constipation, a major diverticulitis trigger.
Drink plenty of water. Adequate hydration softens stool, making it easier to pass and reducing strain on your digestive system.
Engage in regular physical activity. Daily walks or other moderate exercise improve gut motility and overall health, contributing to better digestive function.
Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity increases pressure on the colon, raising your risk of diverticulitis. Weight management reduces this pressure.
Avoid smoking. Smoking impairs the healing process and increases the inflammation associated with diverticulitis.
Manage stress. Stress can negatively impact your digestive system. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like yoga or meditation into your routine.
Eat smaller, more frequent meals. This reduces the burden on your digestive tract and can alleviate discomfort.
Limit red meat consumption. Studies suggest a link between high red meat intake and diverticulitis. Focus on lean protein sources like poultry and fish.
Avoid straining during bowel movements. Listen to your body and address constipation promptly with fiber and hydration.
Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice. They can help you create a plan that suits your individual needs and health status.