The typical Flagyl (metronidazole) dosage for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is 500 mg three times daily for 10 days. This regimen targets the bacteria effectively, aiming for eradication.
However, remember that dosage adjustments might be necessary based on individual factors. Severe cases or those involving recurrent infections may require higher doses or a longer treatment duration. Your doctor will consider factors such as your kidney function, liver function, and overall health when determining the most appropriate treatment.
Important Note: Never adjust your Flagyl dosage without consulting your physician. Improper use can lead to treatment failure or adverse effects. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed regimen closely.
Potential side effects of Flagyl include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a metallic taste in the mouth. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning side effects. Your doctor will also monitor your progress throughout the treatment, assessing the effectiveness of the medication and making adjustments if needed.
- Flagyl Dosage for C. difficile Infection
- Standard Flagyl Dosage for C. difficile
- Adjusting Flagyl Dosage Based on Severity
- Severe CDI Treatment
- Recurrent CDI
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions
- Alternative Treatments and When to Consult a Doctor
- Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Choosing the Right Treatment
- Additional Considerations
Flagyl Dosage for C. difficile Infection
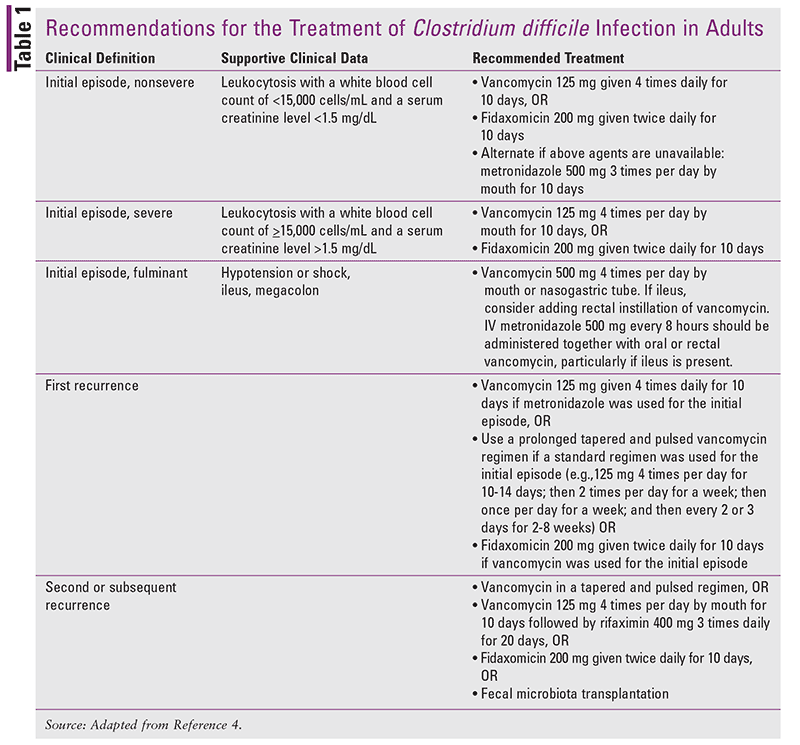
Treatment typically involves a 10-day course of metronidazole (Flagyl). Adults usually receive 500 mg three times daily. Children’s dosages are weight-based; consult a physician for precise instructions.
Severe infections may require higher doses or intravenous administration. Your doctor determines the best approach based on your specific needs.
For recurrent C. difficile infections, a longer course of Flagyl or an alternative antibiotic like vancomycin might be prescribed. Fidaxomicin is another option for recurrent infections.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Do not adjust the dosage without consulting your physician. Report any side effects immediately.
This information does not replace professional medical advice. See your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of C. difficile infection.
Standard Flagyl Dosage for C. difficile
The typical dosage for treating C. difficile infection (CDI) with metronidazole (Flagyl) is 500mg three times daily for 10-14 days. This regimen targets the infection effectively for most patients.
For severe cases, or if the infection doesn’t respond to the standard dose, your doctor might adjust the dosage or duration of treatment. They may increase the frequency to four times daily, or extend the treatment period beyond two weeks. Intravenous administration might be necessary in severe cases.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. They will tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs and health condition. Never alter your medication dosage without consulting your physician. This ensures you receive the most appropriate treatment for your particular circumstances.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of CDI. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health situation.
Adjusting Flagyl Dosage Based on Severity
Treatment for C. difficile infection (CDI) with metronidazole (Flagyl) varies depending on the severity of the infection. Mild to moderate CDI typically responds to a 500mg dose administered three times daily for 10-14 days.
Severe CDI Treatment
For severe CDI, characterized by high fever, significant leukocytosis, or toxic megacolon, a higher dose or a different antibiotic may be necessary. Consult your physician immediately, as intravenous treatment with vancomycin or fidaxomicin may be more appropriate in these cases. Higher doses of Flagyl alone are rarely recommended for severe CDI and may not be effective. Your doctor will determine the most effective course of action based on your specific situation and test results.
Recurrent CDI
If the infection recurs after an initial course of Flagyl, different treatment strategies must be considered. A second course of Flagyl might be used, but often vancomycin or fidaxomicin are preferred for recurrent CDI to minimize the risk of further recurrence. Duration and dosage for recurrent CDI will be determined by your doctor.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions
Metronidazole, the active ingredient in Flagyl, can cause several side effects, though many are mild and temporary. Common ones include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Less frequent, but still possible, are metallic taste in the mouth and headache.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These are often manageable with smaller, more frequent doses or by taking the medication with food.
- Diarrhea: While usually mild, persistent or severe diarrhea should be reported to your doctor immediately, as it could indicate a more serious problem.
- Metallic Taste: This usually resolves once you finish the course of treatment.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage headaches associated with Flagyl.
Rare but serious side effects include seizures and peripheral neuropathy (numbness or tingling in the extremities). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
Flagyl interacts with several medications. It’s critical to inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking.
- Warfarin (Coumadin): Flagyl can increase the effects of warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Your doctor will likely monitor your INR (international normalized ratio) closely.
- Lithium: Flagyl can raise lithium levels in the blood, potentially leading to lithium toxicity. Your doctor may need to adjust your lithium dosage.
- Alcohol: Combining Flagyl with alcohol can cause a disulfiram-like reaction, characterized by nausea, vomiting, flushing, and headache. Avoid alcohol consumption during and for at least 48 hours after completing your Flagyl treatment.
- Disulfiram (Antabuse): Taking Flagyl and disulfiram together can significantly increase the risk of adverse effects.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, including Flagyl, to discuss potential side effects and interactions specific to your individual health situation.
Alternative Treatments and When to Consult a Doctor
Fidaxomicin is a frequently prescribed alternative to Flagyl for C. difficile infection (CDI). It’s particularly useful for patients with recurrent CDI or those who haven’t responded well to metronidazole (Flagyl). While generally well-tolerated, potential side effects include nausea and diarrhea.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
FMT involves transferring stool from a healthy donor to the patient’s gut to restore healthy gut bacteria. Studies show FMT to be highly effective, especially for recurrent CDI, often exceeding the success rate of vancomycin. However, it carries a small risk of transmitting infections. Your doctor will carefully assess your suitability for FMT.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Contact your physician immediately if you experience:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Severe abdominal pain | Intense pain requiring immediate medical attention. |
| Bloody diarrhea | Presence of blood in stool, suggesting serious complications. |
| High fever | Temperature significantly above 101°F (38.3°C), a sign of systemic infection. |
| Dehydration | Signs include excessive thirst, dizziness, and decreased urination. |
Choosing the Right Treatment
Your doctor will consider your medical history, the severity of your infection, and your response to previous treatments to determine the most appropriate course of action. Don’t self-treat CDI; a proper diagnosis and individualized treatment plan are vital for recovery.
Additional Considerations
Certain factors influence treatment choice, including pregnancy, age, and other existing health conditions. Open communication with your doctor ensures you receive the best care possible. Prompt treatment is crucial for preventing severe complications.