Need a concise overview of double-strength doxycycline? This guide provides practical information, focusing on usage, dosage, and potential side effects. We’ll cut straight to the specifics, offering clear explanations and avoiding unnecessary jargon.
Doxycycline, a common antibiotic, is sometimes prescribed in double doses (dbl doxycycline) for specific bacterial infections. This higher dosage often accelerates treatment and enhances effectiveness against resistant strains. However, increased dosage also raises the likelihood of certain side effects, which we’ll explore in detail.
Remember: Always consult your physician before starting any medication, including double-strength doxycycline. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your health condition and individual needs. They will also discuss potential drug interactions and any necessary precautions. This information is for educational purposes and does not substitute professional medical advice.
This guide covers: Typical usage scenarios for dbl doxycycline, recommended dosages, potential side effects (including their frequency and severity), and what to expect during and after treatment. We aim to provide a clear and concise resource for better understanding this specific medication regimen.
- Dbl Doxycycline: A Detailed Overview
- Absorption and Distribution
- Efficacy and Indications
- Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Monitoring and Management
- What is Dbl Doxycycline and its Composition?
- Factors Influencing Dbl Doxycycline Dosage
- Understanding Your Prescription
- Mechanism of Action: How Dbl Doxycycline Works
- Approved Indications and Uses for Dbl Doxycycline
- Treatment of Infections
- Important Considerations
- Off-Label Uses
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Dbl Doxycycline
- Typical Dosing Regimens
- Administration
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects
- Common Side Effects and Potential Adverse Reactions
- Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid with Dbl Doxycycline
- Precautions and Contraindications for Dbl Doxycycline Use
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Specific Conditions
- Potential Side Effects
- Medication Interactions
- Monitoring
- Alternatives
- Overdose and Emergency Management for Dbl Doxycycline
Dbl Doxycycline: A Detailed Overview
Doxycycline, administered twice daily (dbl doxycycline), offers a different pharmacokinetic profile compared to once-daily regimens. This impacts its efficacy and side effect profile, necessitating careful consideration for specific infections.
Absorption and Distribution
Twice-daily dosing maintains higher minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) compared to once-daily dosing, potentially improving treatment of infections with bacteria exhibiting high MICs for doxycycline. However, higher peak serum concentrations might also increase the risk of side effects.
Efficacy and Indications
While the exact clinical benefit of dbl doxycycline over once-daily dosing isn’t universally established for all infections, it often shows improved outcomes in severe or complicated cases. This is particularly relevant for infections like Lyme disease or severe acne, where achieving consistently high drug levels is crucial. Consult prescribing information for specific indications and dosages.
Side Effects
Common side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, can be more frequent with dbl doxycycline due to higher peak concentrations. Photosensitivity is another potential concern. Patients should be informed about these risks and advised on mitigation strategies such as sunscreen use and reporting any unusual symptoms promptly to their healthcare provider.
Drug Interactions
Doxycycline’s interactions with other medications remain the same regardless of dosing frequency. Interactions with antacids, calcium supplements, and some antibiotics can significantly reduce doxycycline absorption. Always provide your doctor a complete medication list to avoid unexpected interactions.
Contraindications and Precautions
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should use doxycycline with caution, as it can cause adverse effects on the developing fetus and infant. Patients with known hypersensitivity to tetracyclines should not use doxycycline. Kidney or liver impairment might require dosage adjustment. A physician must assess suitability based on individual patient factors.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring for treatment response and side effects is recommended, especially during the initial phase of therapy. Patients should report any concerning symptoms immediately. Clinical judgment and patient-specific factors guide the decision of whether dbl doxycycline is the most appropriate treatment option.
What is Dbl Doxycycline and its Composition?
Dbl Doxycycline refers to a dosage regimen involving two doses of doxycycline. This isn’t a specific branded medication; rather, it describes a doctor’s prescribed treatment plan. The composition is simply two doses of doxycycline, a common antibiotic, typically administered as tablets or capsules. Each dose contains a specified amount of doxycycline hyclate or monohydrate, depending on the formulation. Consult your prescription for the exact amount of doxycycline in each dose.
Factors Influencing Dbl Doxycycline Dosage
The precise amount of doxycycline in each dose, and the timing of administration, depends entirely on your specific medical needs and your doctor’s diagnosis. These factors include the type of infection, your weight, and potential drug interactions. Always follow the dosage instructions precisely, as deviating from the prescribed regimen could impair treatment effectiveness. Your doctor will provide a detailed plan outlining the exact amount of doxycycline for each dose, the frequency of administration, and the overall duration of treatment.
Understanding Your Prescription
Your prescription will clearly state the total amount of doxycycline you’ll receive across your two doses. It should also specify the form of the drug (tablet or capsule) and the frequency of intake. This information is critical for safe and effective treatment. Carefully read and understand your prescription before beginning the medication. If you have any questions, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
Mechanism of Action: How Dbl Doxycycline Works
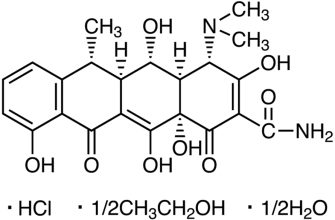
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. It achieves this by binding reversibly to the 30S ribosomal subunit of susceptible bacteria. This binding prevents the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex, halting further polypeptide chain elongation.
Specifically, doxycycline interferes with the A site on the 30S subunit, preventing the addition of new amino acids to the growing peptide chain. This blockage effectively stops bacterial protein production, leading to bacterial cell death.
The “dbl” in “dbl doxycycline” likely refers to a higher dose or a specific formulation (e.g., extended-release). A higher dose increases the concentration of doxycycline at the site of infection, enhancing its inhibitory effect on bacterial protein synthesis. Different formulations can alter the drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, potentially impacting its overall efficacy.
Note: The precise mechanism and effects of any “dbl doxycycline” formulation will depend on its specific characteristics. Consult a healthcare professional or product information for detailed information concerning a particular product.
Important: Doxycycline, like all antibiotics, may cause side effects. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe reactions. Always follow prescribed dosages and complete the entire course of treatment, even if symptoms improve.
Approved Indications and Uses for Dbl Doxycycline
Dbl doxycycline, a formulation delivering two doses of doxycycline in a single tablet, holds FDA approval for several specific bacterial infections. Its use should always be guided by a healthcare professional.
Treatment of Infections
- Acne Vulgaris: Dbl doxycycline effectively treats moderate to severe acne by reducing inflammation and bacterial load. Dosage and duration vary based on individual needs.
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: In conjunction with other antibiotics, dbl doxycycline may treat certain types of pneumonia. This is typically reserved for specific situations determined by a physician.
- Chlamydia Infections: Dbl doxycycline is a common treatment for chlamydia trachomatis infections, including those affecting the genital tract. A single course is generally sufficient, but follow-up testing is crucial.
- Lyme Disease: Doxycycline plays a significant role in treating early-stage Lyme disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. Treatment duration depends on the severity of infection.
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: This severe tick-borne illness also responds to doxycycline treatment. Prompt medical attention is vital to ensure a positive outcome.
Important Considerations
Doxycycline, regardless of formulation, carries potential side effects, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. Patients should discuss potential drug interactions with their doctors. Always follow prescribed dosage and duration precisely. Doxycycline is generally contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Off-Label Uses
While not officially approved, doxycycline may be used off-label by healthcare professionals for specific indications. However, such use necessitates careful consideration and close monitoring by a physician. Examples include the treatment of certain types of infections not listed above. Always consult with your doctor to determine if off-label use is appropriate for your situation.
- Always consult your physician before starting any antibiotic treatment.
- Never self-medicate with doxycycline.
- Complete the full course of medication as prescribed, even if symptoms improve.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Dbl Doxycycline
Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Dosing varies significantly depending on the infection being treated. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Typical Dosing Regimens
- Acne: A common adult dose is 50-100 mg once or twice daily.
- Lyme Disease: Adults often receive 200 mg once daily.
- Chlamydia: A single dose of 100 mg is frequently prescribed.
- Other Infections: Dosage will vary; your doctor will determine the appropriate amount and schedule based on your specific needs and the severity of your infection.
Administration
Doxycycline tablets should be swallowed whole with a full glass of water. Avoid taking them with dairy products, antacids, or iron supplements, as these can reduce absorption.
Take the medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels in your bloodstream. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double the dose to make up for a missed one.
Important Considerations
Potential Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Photosensitivity
Report any significant side effects to your doctor immediately. This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or altering any medication regimen.
Common Side Effects and Potential Adverse Reactions
Doxycycline, while generally well-tolerated, can cause several side effects. Most are mild and temporary. However, some reactions require immediate medical attention.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and upset stomach. These usually resolve without intervention, but if symptoms persist or worsen, consult your doctor. Proper hydration helps manage these gastrointestinal issues.
Less frequent, but still possible, are reactions such as: sun sensitivity (increased risk of sunburn), yeast infections (particularly in women), and esophageal irritation (especially if taken without enough water).
Serious, though rare, adverse reactions include:
| Adverse Reaction | Symptoms | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Reaction | Hives, swelling, difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical help. This is a medical emergency. |
| Increased pressure in the skull (pseudotumor cerebri) | Headache, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting | Contact your doctor immediately. This requires prompt attention. |
| Liver problems | Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes), dark urine, abdominal pain | Seek immediate medical care. This may indicate serious liver damage. |
| Tooth discoloration (in children) | Yellow or brown staining of developing teeth | Avoid doxycycline in children under 8 years old unless absolutely necessary. |
This information is not exhaustive; other side effects may occur. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including supplements and herbal remedies, to minimize potential drug interactions and complications. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. If you experience any concerning symptoms, seek medical advice without delay.
Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid with Dbl Doxycycline
Avoid concurrent use of Dbl doxycycline with dairy products, antacids containing calcium, magnesium, or aluminum, and iron supplements. These substances bind to doxycycline, reducing its absorption and efficacy. Space the administration of these medications by at least two hours.
Warfarin: Doxycycline can potentiate the anticoagulant effects of warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of INR levels is necessary if you’re taking both medications.
Isotretinoin: Combining doxycycline with isotretinoin raises the risk of intracranial hypertension. This combination should generally be avoided.
Methotrexate: Doxycycline can increase methotrexate levels, potentially leading to toxicity. Monitor for side effects and adjust dosages as needed under medical supervision.
Oral contraceptives: Doxycycline may reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. Consider alternative contraception methods while taking doxycycline.
This information is not exhaustive. Always inform your physician or pharmacist of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, you are taking before starting Dbl doxycycline treatment. They can assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Precautions and Contraindications for Dbl Doxycycline Use
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including herbal supplements, before starting doxycycline. This includes antibiotics, birth control pills, and antacids. Doxycycline can interact with these medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
Avoid prolonged sun exposure and use sunscreen with a high SPF while taking doxycycline. Photosensitivity is a known side effect, increasing your risk of sunburn.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Doxycycline is contraindicated during pregnancy due to potential harm to the developing fetus. It’s also generally avoided during breastfeeding, as it can be excreted in breast milk. Discuss alternative treatments with your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Specific Conditions
Doxycycline should be used cautiously, if at all, in patients with liver or kidney problems. Your doctor will carefully assess the risks and benefits before prescribing. Individuals with esophageal disorders should take the medication with plenty of water and remain upright after ingestion to minimize the risk of esophageal irritation.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less common, but serious, side effects include increased pressure in the skull, difficulty breathing, and severe allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these.
Medication Interactions
| Medication Type | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Birth control pills | Reduced effectiveness |
| Antacids | Decreased absorption of doxycycline |
| Warfarin | Increased bleeding risk |
| Dairy products | May interfere with absorption |
Monitoring
Regular monitoring of liver function may be recommended, especially for those with pre-existing liver conditions or who are taking doxycycline for extended periods. Always report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
Alternatives
If doxycycline is unsuitable, your doctor can discuss alternative antibiotics or treatment options. It’s important to find a medication that works best for your specific condition and health status.
Overdose and Emergency Management for Dbl Doxycycline
Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a doxycycline overdose. Call your local poison control center or emergency services.
Symptoms of a doxycycline overdose can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Esophageal irritation (burning sensation in the esophagus)
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight)
- In severe cases: liver damage, kidney damage, or central nervous system effects.
Treatment for doxycycline overdose focuses on supportive care and managing symptoms. Specific treatments may include:
- Activated charcoal administration to absorb the drug in the gastrointestinal tract. This is most effective if administered within a few hours of ingestion.
- Gastric lavage (stomach pumping), though less commonly used now due to the availability of activated charcoal.
- Intravenous fluids to maintain hydration and address electrolyte imbalances.
- Monitoring of vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
- Treatment of specific symptoms as they arise, such as antiemetics for nausea and vomiting.
- Close monitoring of liver and kidney function tests.
The prognosis for doxycycline overdose generally depends on the amount ingested and the promptness of treatment. Early intervention significantly improves outcomes.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.